- ‘Necro Python’ has returned to relevance with a new Monero mining system and new exploits.
- The authors are following the latest trend of targeting web applications, even if the core functions remain the same.
- The actors have also updated their C2 infrastructure to use fresh and unreported domains.
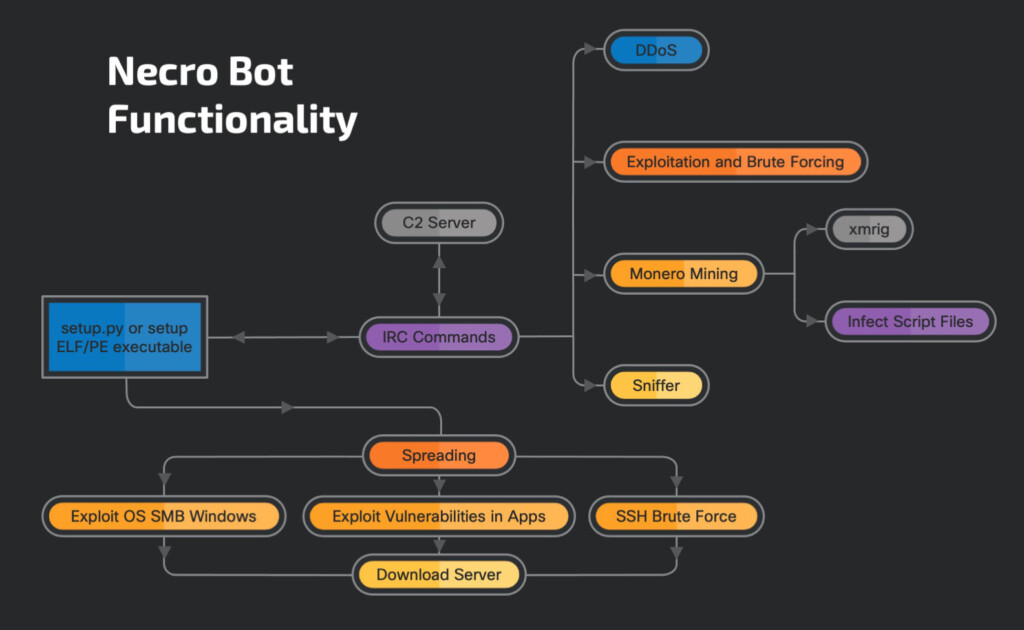
The malware authors known as ‘Necro Python’ have upgraded their attack tool with Monero mining and ten new exploits against VMWare vSphere, SCO OpenServer, Vesta Control Panel, and SMB. Moreover, the hackers behind the campaign that deploys the latest version of ‘Necro Python’ have updated the command and control infrastructure, so the whole operation around the particular malware has been refreshed.
The ‘Necro Python’ bot first appeared online in 2015, but its activity has spiked again since January 2021. The infection process starts with scanning and exploiting one of the hard-coded vulnerabilities, which cover both Windows and Linux OS and apps. The communication with C2 takes place through IRC, and the bot is also capable of launching DDoS attacks, sniff network data, or exfiltrate information from the infected machine.
A notable new part of the code has to do with the XMRig program, which mines Monero, a privacy-focused cryptocurrency. XMRig is only used on Linux-based systems, while Windows victims will get a JavaScript-injection into .htm, .html, .js and .php files. Whenever the user opens the infected application, the miner will run within the browser’s process space, making money for the hackers at the expense of the victim’s system resources and internet data.
The exploitation commands are the following:
- Scanner — Start or stop network scanning.
- Scannetrange — Supply a network as a parameter and used the parameter as a scan range for exploitation.
- Scanstats — Send information about the number of scanned and successfully infected endpoints.
- Clearscan — Clear the status data for the bot.
The backdoor commands of the new ‘Necro Python’ bot have been determined to be the following:
- Revshell — Launch a reverse shell and connect it to the listener set up by the attacker on Linux-based operating systems.
- Shell — Launch a process using process.popen() function.
- Download — Download a file from a supplied URL.
- Execute — First, download, then execute, the downloaded file.
- Update — Update with a new bot version.
- Visit — Visit a supplied URL.
- Dlexe — Download and execute a file.
- Killbypid — Terminate a process with a supplied process ID.
According to Cisco Talos researchers who have the detailed report, the latest exploits and spike in the ‘Necro Python’ bot activity came in May, so it looks like the actors will continue the pushing for now. The main focus remains the mining of Monero, but as long as information stealing is included in the scope, a lot more can happen through the malware. That’s especially the case if the author opens access to the bot through a MaaS program when they are confident enough.