A cryptomining botnet spotted last year is now targeting and attempting to take control of Jenkins and ElasticSearch servers to mine for Monero (XMR) cryptocurrency.
z0Miner is a cryptomining malware strain spotted in November by the Tencent Security Team, who saw it infecting thousands of servers by exploiting a Weblogic security vulnerability.
Now, the attackers have upgraded the malware to scan for and attempt to infect new devices by exploiting remote command execution (RCE) vulnerabilities impacting ElasticSearch and Jenkins servers.
Probing for servers left unpatched for years
According to a report published by researchers at Qihoo 360’s Network Security Research Lab (360 Netlab), z0Miner is now probing for servers unpatched against vulnerabilities addressed in 2015 and earlier.
The botnet uses exploits targeting an ElasticSearch RCE vulnerability tracked as CVE-2015-1427 and an older RCE impacting Jenkins servers.
After compromising a server, the malware will first download a malicious shell script, starts hunting for and killing previously deployed cryptominers.
Next, it sets up a new cron entry to periodically grab and execute malicious scripts from Pastebin.
The next stage of the infection flow involves downloading a mining kit containing an XMRig miner script, a config file, a starter script, and starting to mine cryptocurrency in the background.
360 Netlab found that one of the Monero wallets used by the z0Miner botnet contains roughly 22 XMR (just over $4600).
However, even if this doesn’t seem like much, cryptomining botnets regularly use more than one wallet to collect illegally earned cryptocurrency that can quickly add up.
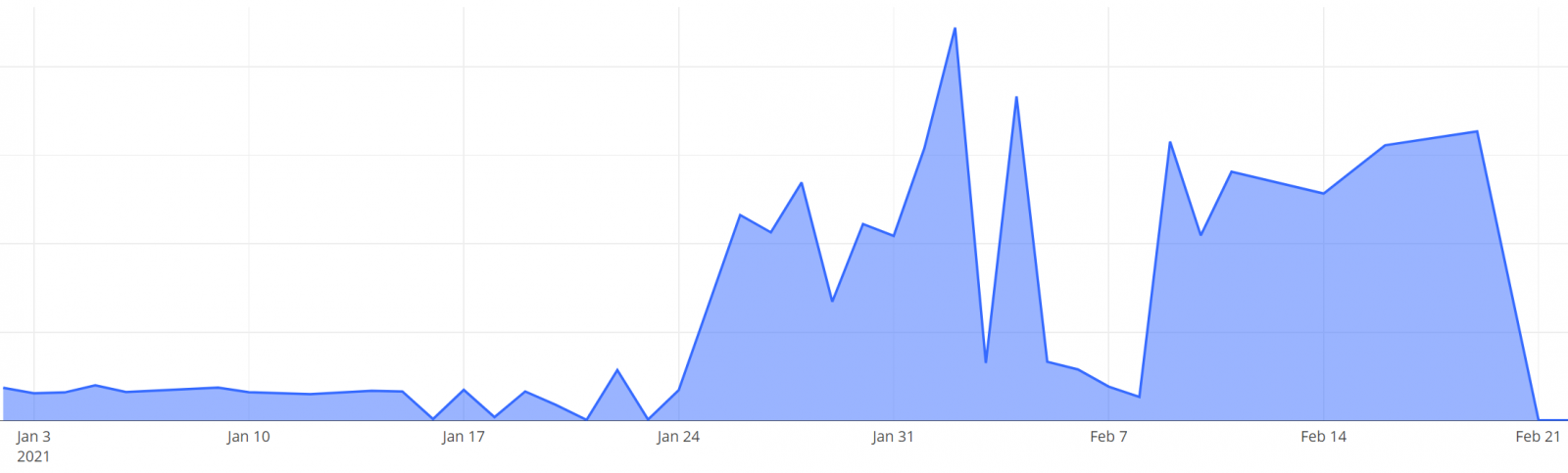
According to honeypot stats shared by 360 Netlab, the z0Miner botnet activity has started picking up again during mid-January after a short break in early-January.
Thousands of devices already compromised
z0Miner became active last year and was spotted by the Tencent Security Team while exploiting two Weblogic pre-auth RCE bugs tracked as CVE-2020-14882 and CVE-2020- 14883 to spread to other devices.
According to Tencent Security Team estimations, the threat actor controlling z0Miner compromised and quickly took over 5,000 servers.
The attackers scanned cloud servers in batches to find unpatched Weblogic servers and compromised them by sending “carefully constructed data packets” to exploit the vulnerable devices.
After compromise, z0Miner used a similar attack logic as the one observed by 360 Netlab researchers, gaining persistence via crontab and starting to mine for Monero.
The z0Miner sample found by Tencent Security Team in November 2020 was also spreading laterally on the network of already compromised devices via SSH.
