Ether (ETH-USD)the currency for the Ethereum blockchain, benefits from a unique set of macroeconomic and technological drivers. The issuance of Ether is slowing down, and the amount of Ether available for trading is being reduced, while demand from investors increases. As a result, the value of Ether will likely increase over the coming years.
How Ether is Different From Bitcoin
The bitcoin blockchain validates, stores, and replicates transaction data across a distributed network of computers. Ethereum takes this idea one step further because it also has the ability to run computer code, known as smart contracts.
Bits on Blocks describes it succinctly:
What bitcoin does for distributed data storage, Ethereum does for distributed data storage plus computations.
While bitcoin (BTC-USD) is basically a form of digital money. Ethereum is a programmable smart contract platform.
Smart contracts can be used for nearly any type of financial transaction. The use of smart contracts, sometimes referred to as decentralized applications, or DApps, can eliminate the need for middleman in financial transactions. Potential applications of decentralized finance could disrupt industries such as insurance, financial derivatives, securities trading and real estate. Ethereum makes decentralized finance possible.
Smart Contract Ecosystem
Ethereum has the first mover advantage as the dominant agreement network for decentralized finance. Several major companies are building products on Ethereum including Nike, Ernst and Young, and Barclays. Board members of the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance include Santander, JP Morgan, and Intel, among others. Organizations that have not yet started blockchain projects are likely to follow the lead of these organizations, rather than taking a greater risk on less tested platforms.
The following chart shows how dominant Ethereum is compared to other platforms for smart contracts/DApps.
Source: State of the DApps
Ethereum has gone through several minor upgrades since it launched in 2015. Now it is in the process of launching its biggest upgrade, to a new system called Ethereum 2.0. The implementation of will move the system from a proof of work to proof of stake consensus. This is a more energy efficient than proof of work because it depends on people posting collateral, rather than making massive calculation requiring powerful computers. It will also enhance security and decentralization.
Perhaps most importantly for Ether investors, Ethereum 2.0 will make the platform more scalable, allowing more and more transactions to be conducted on its network. There is some risk that there will be technical problems with the implementation. However, if it succeeds it will increase the value of the Ethereum ecosystem, and combined with the other supply demand dynamics, it could drive the price of Ether higher.
Supply
Unlike Bitcoin, Ether does not have a hard cap on issuance. Instead it issues just enough tokens to keep the network functional. Critics of Ethereum argue that this prevents it from being a reliable store of value. However fixed amounts of coins are added each year, so as the Ethereum Whitepaper notes, over time the supply growth rate for Ether will trend towards zero. In fact, the issuance rate of Ether over the next few years will be even slower than that in bitcoin.
This chart shows the historical and projected issuance rates of Ether and BTC.
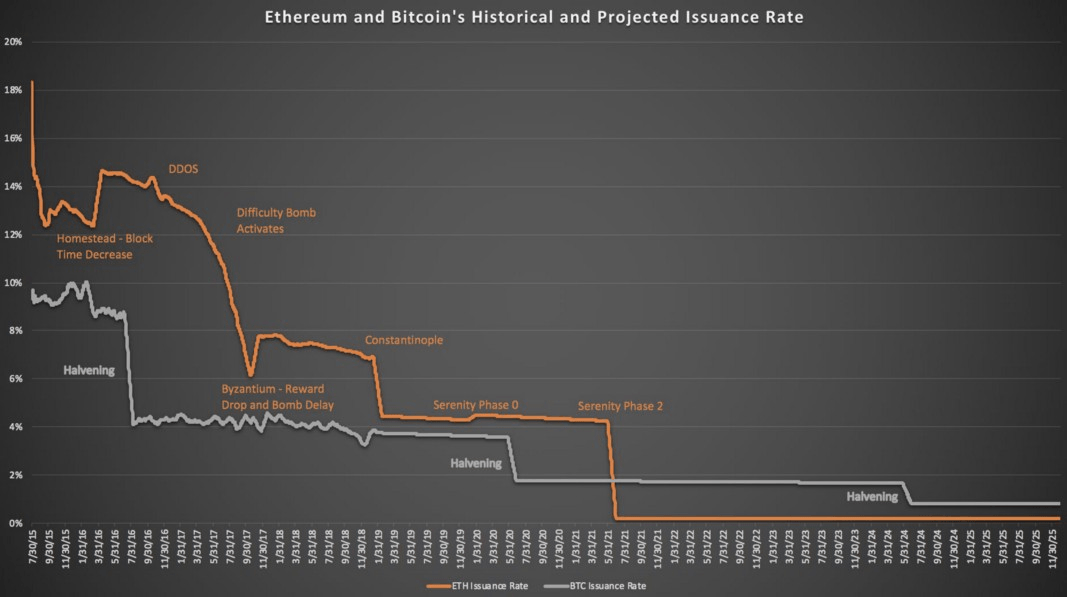
Source: Nicoya Research
While the issuance rate of Ether declines, two factors will cause an increasing proportion of it to be locked up, and not available for trading. First of all, decentralized finance apps are built using the Ethereum blockchain, more Ether is locked up for use in smart contracts. Similarly, as existing apps become more popular, the supply of Ether available for traders declines.
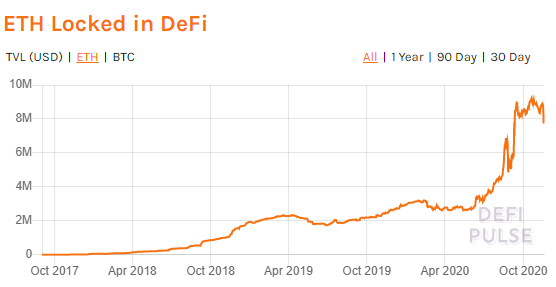
Source: Defipulse
The second factor reducing supply is the impact of Ethereum 2.0 staking This refers to people holding a certain amount of Ether locked up as collateral to participate in the Ethereum 2.0 network. This Ether that is staked cannot be accessed until the completion of Phase 2 of the implementation, likely several years from now. Effectively, this staking process will reduce the amount of Ether that is available for speculators and investors to purchase. A lot of people that stake their Ether will likely already be long term holders anyways, but even a small amount of reduced liquidity is significant given Ether has such a small market cap. This aspect of the Ether 2.0 Rollout is bullish for ETH, according Eric Conner at Gnonnis, who was quoted in a recent Coindesk research paper
This shrinking liquid supply will be met by rising demand.
Rising Demand
The Ethereum 2.0 implementation is likely to increase the network value of Ethereum. By improving scaling solutions for Ethereum, it will attract larger institutions to create applications that rely on it. The Ethereum 2.0 implementation will allow people who stake their Ether to earn returns from holding coins, just like holding a bank deposit. This mechanism turns Ether into a positive carry asset and should support Ether’s function as a store of value.
Closely related, the growing institutional acceptance of digital assets that is so central to the near term bitcoin thesis is also positive for ETH. Just as larger institutional investors have invested in bitcoin as a a hedge against fiat currency debasement, they will also turn to Ether as a complement to cash and securities. Ether’s current market cap of ~$53 billion is less than ⅙ that of Bitcoin, but as it becomes larger, it will attract larger institutions, creating a self reinforcing feedback loop. As it becomes easier to purchase cryptocurrencies, more retail investors will also enter the market. Notably. Paypal, recently added Ether access capabilities alongside BTC.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrencies protect against systemic risk because they are outside the system. Like all currencies they depend on some sort of consensus among users, but unlike fiat currency, cryptocurrencies do not depend on the existing institutional architecture. Although BTC has been gaining more attention from mainstream investors, Ether remains somewhat under the radar. Currently Ether’s market cap is ⅙ of Bitcoin. Ether serves as the base layer for a smart contract ecosystem that has the potential to upend or replace many existing financial institutions. As technical factors reduce the amount of Ether available for trading, and more people start to use smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain to conduct transactions, the value of Ether could increase substantially.
Disclosure: I am/we are long ETH-USD, BTC-USD. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
