Malicious actors have targeted crypto protocols and exchanges ever since Bitcoin started to gain in both popularity and value back in 2011. However, while on-chain analysis shows such attacks have declined this year, they remain the leading cause of concern for crypto projects.
However, contrary to popular belief, Ethereum-based applications and tokens have not been attacked as much as other ETH “killers,” a recently held study showed.
EOS: The most attacked network
As per a report by the Atlas VPN team provided to CryptoSlate, hackers have stolen over $13.6 billion through 330 blockchain hacks over the lifetime of the young crypto industry.
The biggest hit has been suffered by projects building on EOS, the world’s 13th-largest blockchain network. dApps building on the platform have suffered over 117 breaches and make up 36% of all blockchain-related breaches. Attackers have caused over $28.28 million in losses, approximately $241,785.8, per single breach.
Next on the list are Tron dApps. Atlas researchers said cybercriminals have launched over 21 successful Tron dApp attacks, stealing $1.22 million or around $58,301.64 per breach in the process. This aspect has arguably caused the Tron network to fall out of favor among investors — apart from the criticism it faces from being a “centralized” token entity.
Interestingly, Ethereum-based tokens have had the “least amount of successful hacks” among all popular blockchain protocols. However, the network has suffered the maximum losses: Hackers have stolen over $1.14 billion from just 8 breaches, indicating that while the security level is higher, the amount of funds at risk is even higher.
Poor code leading to Ethereum dApp hacks
Dmytro Volkov, CTO of cryptocurrency exchange CEX.IO, told CryptoSlate that Ethereum applications, such as this year’s booming DeFi market, attract both hype and funds to the oft-unaudited platform, in turn becoming a ripe target for attackers.
“Large capital began to attract hackers and fraudsters who, under other circumstances, would probably not have been interested in a complex hack if there was no expectation of large profits,” Volkov noted.
He added that issues in a project’s source code were the leading cause of all Ethereum-based vulnerabilities:
“Hackers began to attack projects more actively, and most of the dapp hacks are based on exploiting vulnerabilities that appeared due to errors in the source code.”
However, Volkov stated that the projects that did survive became more resilient as they “corrected their mistakes and became an example for other projects on how to avoid such errors in their codes.”
Crypto exchanges, wallets, and blockchains hit hard
Apart from individual blockchains, crypto-businesses have suffered the wrath of attackers as well. Exchanges account for the top of such attacks, with hackers launching 87 successful attacks and collectively netting over $4.82 billion in lifetime earnings.
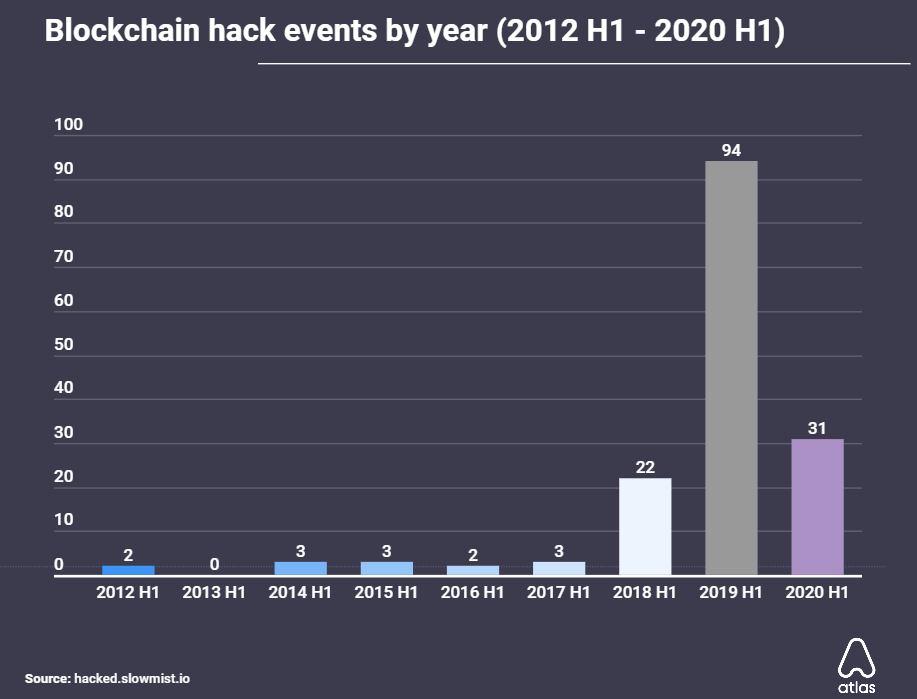
Meanwhile, crypto wallets have been the most profitable for attackers. Data shows that only 36 breaches over the past 8 years have together amounted to $7.19 billion in losses — over $200 million per breach.
Lastly, popular blockchains themselves have been the target of several attacks, with at least 28 successful attacks since 2012. Hackers have profited over $45.8 million from such instances, with targets including Bitcoin Gold, Ethereum Classic, and Litecoin Cash.
Like what you see? Subscribe for daily updates.
